01 May The Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system or ECS is a biological system of receptors and neurotransmitters found throughout the brains and nervous systems. Within all mammalian species, the ECS is the largest biological system of receptors in the body. It holds the potential to revolutionize the ways in which we view health and wellness understanding the ECS. The ECS was discovered in the 1990s with scientists studying how cannabis produced effects on the body’s endocannabinoids and receptors they bind to. Endocannabinoids exist throughout the body in the nervous system, immune cells, organs, the brain and connective tissues. The ECS permeates all 11 main physiological systems in the body working to handle the many functions necessary for survival. The ECS tunes our vital physiological functions and promotes homeostasis affecting everything from sleep, appetite, pain, inflammation, memory, mood, and reproduction. The ECS helps to regulate homeostasis across all the major physiological systems ensuring they’re all working in harmony with one another.
Components of the ECS
The ECS comprises three primary components: endocannabinoids, enzymes, and receptors. Cannabinoids are groups of active compounds that interact with ECS receptors.
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids are produced naturally inside of the body or compounds found outside the body like CBD and THC. CBD and THC are exogenous cannabinoids and known as phytocannabinoids which means that it originates from plants. Cannabinoids act as the keys within the endocannabinoid system while receptors act like locks. Every time one key fits into one lock the lock causes an effect to occur in the body. The two main types of endocannabinoids found in the body are anandamide and 2-AG. 2-AG is the most prevalent endocannabinoid responsible for managing appetite, pain response and immune system functions. Anandamide, (Sanskrit for “bliss”) is responsible for runner’s eye and the blissful states that come from structured play yoga and meditation as well as being triggered by other foods such as chocolate.
Enzymes
Enzymes are any substance within the body that cause chemical reactions to occur. Enzymes act within the ECS to recycle used endocannabinoids after the body is through with them.

Receptors
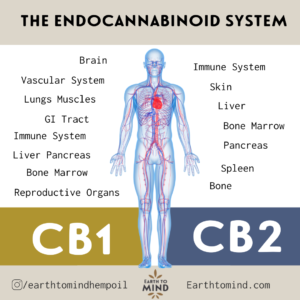
Receptors receive the messages transmitted by cannabinoids. There are two main types of receptors CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors exist in the brain and spinal cord working to regulate appetite memory and to reduce pain. CB2 receptors are within the immune system and many other areas of the body working primarily to reduce inflammation throughout the body. Inflammation is a process the body undergoes to heal infected or damaged areas in the body inflammation is a main cause of many different medical conditions.
Conclusion
In each part of the body the endocannabinoid system performs different tests, but the ECS always has one goal in mind: homeostasis. Your ECS works to keep a stable internal environment to counter act the inevitable changes and variations in the external environment. Interested in more ways to keep your body in balance? Check out our family of brands for more ways to wellness!